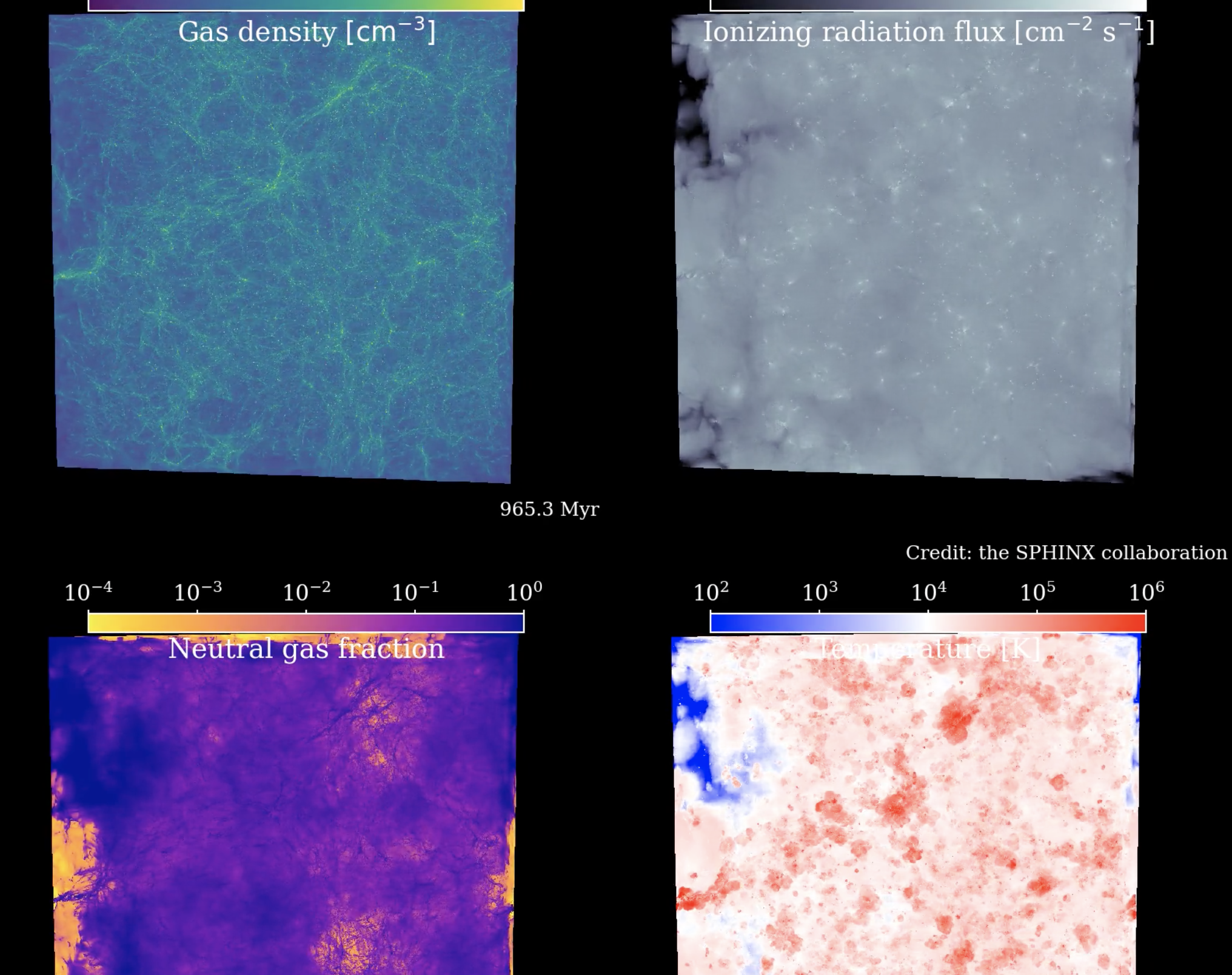
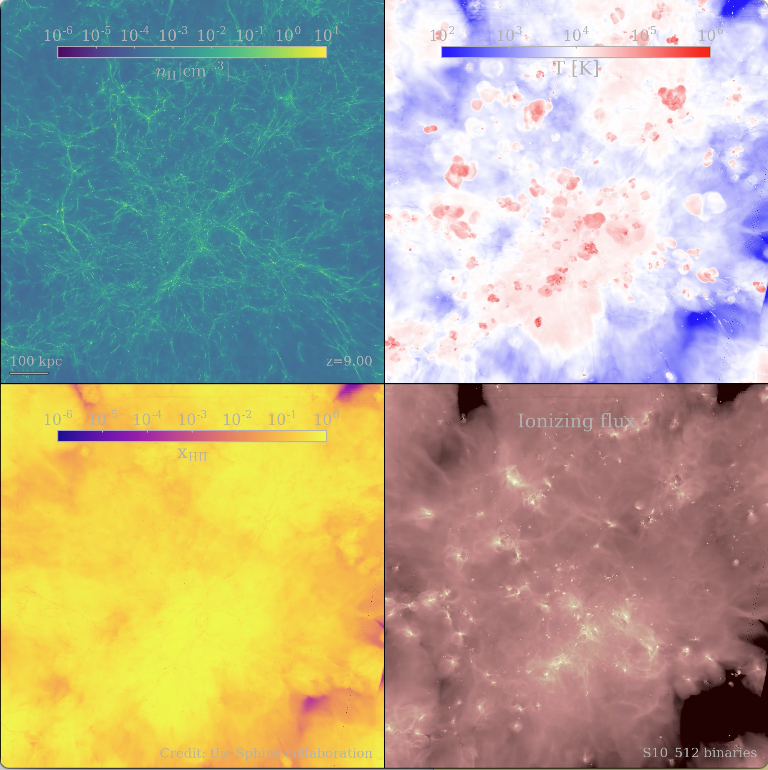
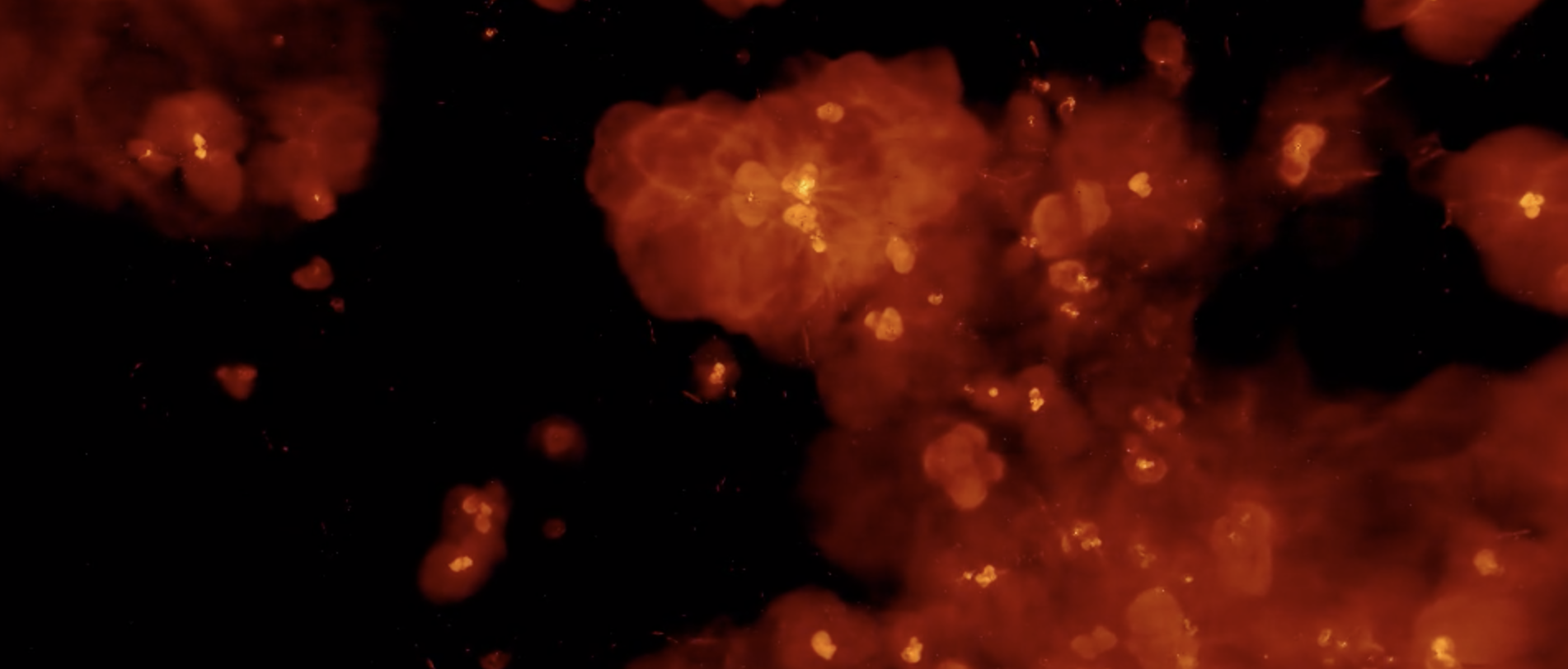
The SPHINX suite of cosmological radiation-hydrodynamical simulations is designed to simultaneously capture large-scale reionization and the escape of ionizing radiation from thousands of resolved galaxies during the first billion years of the Universe. Our volumes resolve haloes down to the atomic cooling limit and model the inter-stellar medium of galaxies with ≈ 10 parsec resolution. The project has numerous goals in improving our understanding of reionization and making predictions for future observations.
Core members of the team are:
- Joakim Rosdahl (PI), Centre de Recherche Astrophysique de Lyon
- Jérémy Blaizot, CRAL
- Thibault Garel, Geneva University
- Martin Haehnelt, Cambridge University
- Harley Katz, Oxford University
- Taysun Kimm, Yonsei University
- Sergio Martin-Alvarez, Cambridge University
- Léo Michel-Dansac, CRAL
- Pierre Ocvirk, Observatoire Astronomique de Strasbourg
- Romain Teyssier, University of Zürich
Ойыншылар бағалайды Vavada casino үшін алуан ойындар мен жомарт бонустар. Казино ұсынады түрлі нұсқаларын іздеп кім үшін классикалық және жаңа өрістер. Алаңы, сондай-ақ, қолдайды лездік депозиттер мен қорытындылар қауіпсіздігін қамтамасыз ете отырып, барлық транзакциялар.
We gratefully acknowledge the following entities for making the SPHINX project possible:
- PRACE, for providing 100 million cpu-hours for running SPHINX simulations on the Supermuc and Juwels supercomputers.
- GENCI, for providing tens of millions of cpu-hours to run SPHINX simulations on the Occigen and Joliot Curie supercomputers.
- CSAA, for financial support to acquire SPHINX simulation storage
- PNCG, for sponsoring collaboration workshops.
- CNRS and NRF, for providing PRC travel grants between Europe and South Korea to strengthen our collaboration and add collaborative partners.
- Partenariat Hubert Curien, for providing travel grants to Japanese collaborative partners.
- The Common Computing Facility (CCF) of the LABEX Lyon Institute of Origins, for providing acess to machines for analysing and post-processing SPHINX outputs